
Science - Class 9

Is Matter Around Us Pure - Questions
Q39. Smoke and fog both are aerosols. In what way are they different?
Q40. You are given two samples of water labelled as ‘A’ and ‘B’. Sample ‘A’ boils at 100°C and sample ‘B’ boils at 102°C. Which sample of water will not freeze at 0°C? Comment
Q41. What are the favourable qualities given to gold when it is alloyed with copper or silver for the purpose of making ornaments?
Q42. Classify the following into elements, compounds and mixtures.
(a) Sodium
(b) Soil
(c) Sugar solution
(d) Silver
(e) Calcium carbonate
(f) Tin
(g) Silicon
(h) Coal
(i) Air
(j) Soap
(k) Methane
(l) Carbon dioxide
(m) Blood
Q43. List any two applications of crystallization.
Q44. How Tyndall effect can be observed in the canopy of a dense forest?
Or
What effect is observed when sunlight passes through the canopy of a dense forest? Explain
Q45. Which method is used to separate two miscible liquids?
Q46. What types of mixtures are separated by the technique of crystallisation?
Q47. The ‘sea-water’ can be classified as a homogeneous as well as heterogeneous mixture. Comment
Q48. List the two conditions essential for using distillation as a method for separation of the components from a mixture.
Q49. Can we separate alcohol dissolved in water by using a separating funnel? If yes, then describe the procedure. If not, explain.
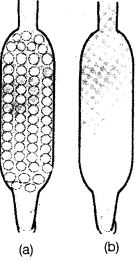
Q50. Which of the tubes in Figure (a) and (b) will be more effective as a condenser in the distillation apparatus?
Q51. Sucrose (sugar) crystals obtained from sugarcane and beetroot are mixed together. Will it be a pure substance or a mixture? Give reasons for the same.
Q52. Give some examples of Tyndall effect observed in your surroundings?
Q53. How would you confirm that a colourless liquid given to you is pure water?
Q54. How do solution and gel differ from each other? Give one example for each.
Q55. What is homogeneous mixture? Give examples.