
Science - Class 9

Topic outline
-
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science- Is Matter Around Us Pure (Chemistry), NCERT Textbook Solutions for Class 9 Science, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Chemistry, Is Matter Around Us Pure - Class 9th NCERT Solutions Science, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Chemistry Science Chapter 2 - Is Matter Around Us Pure, Science - Chemistry - Class 9 (CBSE/NCERT) - Chapter 2 – Is Matter Around Us Pure – Questions and Answers/Notes/Worksheets, CBSE Class 9 - Chemistry – Chapter 2 - Is Matter Around Us Pure Practice Pages, Extra Question and Answer based on NCERT for Class 9th, Science Chemistry, CBSE Grade IX free Worksheets PDF Is Matter Around Us Pure exemplar question answer, NCERT Book question answer, Science Question bank on Is Matter Around Us Pure for ninth standard, Is Matter Around Us Pure, How can we separate a mixture of salt and ammonium chloride? Why alloy is considered as a mixture? Why is an alloy a mixture? Write the principle and applications of separating funnel. (a) Under which category of mixtures will you classify alloys and why? (b) A solution is always a liquid. Comment. (c) Can a solution be heterogeneous? What is crystallization? Why is crystallization better than evaporation? What are the components of a Colloidal Solution? How can we obtain different gases from air? What is a concentration of a solution? You are provided with a mixture containing sand, iron filings, ammonium chloride and sodium chloride. Describe the procedures you would use to separate these constituents from the mixture? A group of students took an old shoe box and covered it with a black paper from all sides. They fixed a source of light (a torch) at one end of the box by making a hole in it and made another hole on the other side to view the light. They placed a milk sample contained in a beaker/tumbler in the box as shown in the Figure. They were amazed to see that milk taken in the tumbler was illuminated. They tried the same activity by taking a salt solution but found that light simply passed through it? (a) Explain why the milk sample was illuminated? Name the phenomenon involved. (b) Same results were not observed with a salt solution. Explain. (c) Can you suggest two more solutions which would show the same effect as shown by the milk solution? Differentiate between elements and compounds. Which of the following are chemical changes? (a) Growth of a plant (b) Rusting of iron (c) Mixing of iron filings and sand (d) Cooking of food (e) Digestion of food (f) Freezing of water (g) Burning of a candle
-
Is Matter Around Us Pure
Q67. How can we separate a mixture of salt and ammonium chloride?
Ans. Ammonium chloride changes directly from solid to gaseous state on heating. So, to separate such mixtures that contain a sublimable volatile component from a non-sublimable impurity (salt in this case), the sublimation process is used. Some examples of solids which sublime are ammonium chloride, camphor, naphthalene and anthracene.
Q68. Why alloy is considered as a mixture?
Or
Why is an alloy a mixture?
Ans. Alloys are homogeneous mixtures of metals and cannot be separated into their components by physical methods. But still, an alloy is considered as a mixture because it shows the properties of its constituents and can have variable composition. For example, brass is a mixture of approximately 30% zinc and 70% copper.
Q69. Write the principle and applications of separating funnel.
Ans. The principle is that immiscible liquids separate out in layers depending on their densities.
Applications
• To separate mixture of oil and water.
• In the extraction of iron from its ore, the lighter slag is removed from the top by this method to leave the molten iron at the bottom in the furnace.
Q70. (a) Under which category of mixtures will you classify alloys and why?
(b) A solution is always a liquid. Comment.
(c) Can a solution be heterogeneous?
Ans. (a) Alloys are homogeneous mixtures of metals and cannot be separated into their components by physical methods.
(b) Usually we think of a solution as a liquid that contains either a solid, liquid or a gas dissolved in it. But, we can also have solid solutions (alloys) and gaseous solutions (air).
(c) No, A solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or more substances.
Q71. What is crystallization? Why is crystallization better than evaporation?
Ans. Crystallisation is a process that separates a pure solid in the form of its crystals from a solution. Crystallisation technique is better than simple evaporation technique as –
• some solids decompose or some, like sugar, may get charred on heating to dryness.
• some impurities may remain dissolved in the solution even after filtration. On evaporation these contaminate the solid.
Q72. What are the components of a Colloidal Solution?
Ans. The components of a colloidal solution are the dispersed phase and the dispersion medium. The solute-like component or the dispersed particles in a colloid form the dispersed phase, and the component in which the dispersed phase is suspended is known as the dispersing medium. Colloids are classified according to the state (solid, liquid or gas) of the dispersing medium and the dispersed phase.
Q73. How can we obtain different gases from air?
Ans. Air is a homogeneous mixture and can be separated into its components by fractional distillation. The air is compressed by increasing the pressure and is then cooled by decreasing the temperature to get liquid air. This liquid air is allowed to warm-up slowly in a fractional distillation column, where gases get separated at different heights depending upon their boiling points.
Q74. What is a concentration of a solution?
Ans. The concentration of a solution is the amount of solute present in a given amount (mass or volume) of solution, or the amount of solute dissolved in a given mass or volume of solvent.
Concentration of solution = Amount of solute/Amount of solution
Or
Amount of solute/Amount of solvent
Q75. You are provided with a mixture containing sand, iron filings, ammonium chloride and sodium chloride. Describe the procedures you would use to separate these constituents from the mixture?
Ans. Step 1: Separate iron filings with the help of magnet.
Step 2: Separate ammonium chloride from sand and sodium chloride by sublimation.
Step 3: Separate sand from sodium chloride by filtration after dissolution.
Step 4: Separate sodium chloride by evaporation.
Q76. A group of students took an old shoe box and covered it with a black paper from all sides. They fixed a source of light (a torch) at one end of the box by making a hole in it and made another hole on the other side to view the light. They placed a milk sample contained in a beaker/tumbler in the box as shown in the Figure. They were amazed to see that milk taken in the tumbler was illuminated. They tried the same activity by taking a salt solution but found that light simply passed through it?
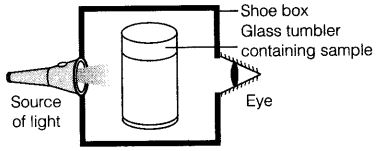
(a) Explain why the milk sample was illuminated? Name the phenomenon involved.
(b) Same results were not observed with a salt solution. Explain.
(c) Can you suggest two more solutions which would show the same effect as shown by the milk solution?
Ans. (a) Milk is a colloidal solution. Its particles are big enough to scatter the light passing through it. The phenomenon observed is called “Tyndall effect”.
(b) Salt solution is a true solution i.e., solute particle size is too small to scatter the light, hence, it does not show “Tyndall effect”.
(c) soap solution, blood
Q77. Differentiate between elements and compounds.
Ans.
Elements
Compounds
1. Cannot be broken down to simpler substances.
1. Have fixed composition. Can be broken down into elements by chemical or electrochemical reactions.
2. For example: copper, oxygen, iron, hydrogen, mercury etc.
2. For example: water, methane, sugar, salt etc.
Q78. Which of the following are chemical changes?
(a) Growth of a plant
(b) Rusting of iron
(c) Mixing of iron filings and sand
(d) Cooking of food
(e) Digestion of food
(f) Freezing of water
(g) Burning of a candle
Ans. Out of given, following are the examples of chemical changes:
(a) Growth of a plant
(b) Rusting of iron
(c) Cooking of food
(d) Digestion of food
(e) Burning of a candle
-