
Science - Class 8 (C ...

Topic outline
-
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science PDF free download, NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics, to Study online or download free in PDF form. NCERT Textbook Answers of class 8 science chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics. CBSE Class 8 Science Notes , Question Answers provided for NCERT Science Textbook for Class 8. Class 8 Science Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics Exercises Answers, Class 8th Science, Class 8 Science exams, class 8 science notes, science class 8 notes, ncert class 8 science, Synthetic Fibres and Plastics class 8 notes pdf, NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics, Download NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science, CBSE Science Class 8 Chapter Wise Solved Q&ans, Learn 8th grade science, Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics, NCERT Solutions for Class 8th Science Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics, CBSE Class 8 Science Chapter 3 - Synthetic Fibres and Plastics, Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics class 8 science, Science-Class 8 (CBSE/NCERT)-Chapter 3- Synthetic Fibres and Plastics - Questions and Answers/Notes/Worksheets – 1 Tags: Class VIII - Synthetic Fibres and Plastics, CBSE Grade 8 Science Synthetic Fibres and Plastics, Science - Class 8- Synthetic Fibres and Plastics, NCERT Solutions for Class 8th: Ch 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics, Class 8 CBSE Science Synthetic Fibres and Plastics, CBSE class 8 science Synthetic Fibres and Plastics, Grade 8 –Science - CBSE / NCERT – Synthetic Fibres and Plastics Question Bank for eighth class, Question and Answers free worksheet PDF on Synthetic Fibres and Plastics, Practice page and Important question and Extra question on Synthetic Fibres and Plastics for eighth standard, Name two polyester fabrics and write their uses. Why should we not wear synthetic clothes while working in in the kitchen or in a laboratory? Differentiate between natural and synthetic fibres. “Even though plastics are very useful, they are not environment friendly.” Justify the statement. ‘Avoid plastics as far as possible’. Comment on this advice. Suggest some ways to solve plastic pollution. How can pollution due to plastics be solved? Explain the difference between the thermoplastic and thermosetting plastics. Why we should not throw polybags in the water bodies or on the road? Categorise the materials of the following products into ‘can be recycled’ and ‘cannot be recycled’: Telephone instruments, plastic toys, cooker handles, carry bags, ball point pens, plastic bowls, plastic covering on electrical wires, plastic chairs, electrical switches. Describe an activity to show that thermoplastic is a poor conductor of electricity. Differentiate between biodegradable and non-biodegradable materials.
-
Synthetic Fibres and Plastics
Q54. Name two polyester fabrics and write their uses.
Ans. Polyester fabrics
i. Terylene is a popular polyester. It can be drawn into very fine fibres that can be woven like any other yarn.
ii. PET is a very familiar form of polyester. It is used for making bottles, utensils, films, wires and many other useful products.
Q55. Why should we not wear synthetic clothes while working in in the kitchen or in a laboratory?
Ans. Synthetic fibres melt on heating. If the clothes catch fire, it can be disastrous. The fabric melts and sticks to the body of the person wearing it. We should, therefore, not wear synthetic clothes while working in in the kitchen or in a laboratory.
Q56. Differentiate between natural and synthetic fibres.
Ans. Difference between natural and synthetic fibres
Natural Fibres
Synthetic Fibres
1. Natural fibres are obtained from plants and animals.
1. Synthetic fibres are made by human beings by chemical processing of petrochemicals.
2. Example: cotton, wool, silk, etc.
2. Example: rayon, nylon, polyester and acrylic
Q57. “Even though plastics are very useful, they are not environment friendly.” Justify the statement.
Ans. Since plastic takes several years to decompose, it is not environment friendly. It causes environmental pollution. Besides, the burning process in the synthetic material is quite slow and it does not get completely burnt easily. In the process it releases lots of poisonous fumes into the atmosphere causing air pollution.
Q58. ‘Avoid plastics as far as possible’. Comment on this advice.
Ans. Since plastic takes several years to decompose, it is not environment friendly. It causes environmental pollution. Besides, the burning process in the synthetic material is quite slow and it does not get completely burnt easily. In the process it releases lots of poisonous fumes into the atmosphere causing air pollution. Thus, we should avoid plastic as far as possible.
Q59. Suggest some ways to solve plastic pollution.
Or
How can pollution due to plastics be solved?Ans. Ways to solve plastic pollution
i. Avoid the use of plastics as far as possible.
ii. Make use of bags made of cotton or jute when you go for shopping.
iii. The biodegradable and non-biodegradable wastes should be collected separately and disposed off separately.
iv. Recycle the plastic waste.
Q60. Explain the difference between the thermoplastic and thermosetting plastics.
Ans.
Thermoplastic plastics
Thermosetting plastics
1. There some plastic which gets deformed easily on heating and can be bent easily are known as thermoplastics plastics.
1. There are some plastics which when moulded once, cannot be softened by heating. These are called thermosetting plastics.
2. Example: polythene and PVC
2. Example: bakelite and melamine.
Q61. Why we should not throw polybags in the water bodies or on the road?
Ans. We should not throw polybags in the water bodies or on the road because:
i. Cow while eating garbage waste food items swallow the polythene bags and wrappers of food. The plastic material chokes the respiratory system of these animals, or forms a lining in their stomachs and can be the cause of their death.
ii. The polybags carelessly thrown here and there are responsible for clogging the drains, too.
Q62. Categorise the materials of the following products into ‘can be recycled’ and ‘cannot be recycled’:
Telephone instruments, plastic toys, cooker handles, carry bags, ball point pens, plastic bowls, plastic covering on electrical wires, plastic chairs, electrical switches.Ans.
can be recycled
cannot be recycled
telephone instruments
plastic toys
cooker handles
carry bags
electrical switches
ball point pens
plastic bowls
plastic covering on electrical wires
plastic chairs
Q63. Describe an activity to show that thermoplastic is a poor conductor of electricity.
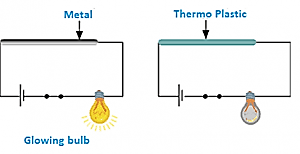
Ans. In order to show that thermoplastic is a poor conductor of electricity, we will design a circuit. For that, we need a bulb, some wires, a battery, a piece of metal and a plastic pipe. After switching on the current, the bulb glows in the former case. In the latter case, the bulb does not glow. Hence a plastic pipe (which is a thermoplastic) is shown to be a poor conductor of electricity.
Q64. Differentiate between biodegradable and non-biodegradable materials.
Ans. Difference between biodegradable and non-biodegradable materials
Biodegradable materials
Non-biodegradable materials
1. A material which gets decomposed
through natural processes, such as
action by bacteria, is called biodegradable.
1. A material which is not easily decomposed by natural processes is termed as non-biodegradable.
2. Example: Peels of vegetable and fruits, leftover foodstuff, Paper, Cotton cloth, Wood, Woollen clothes etc.
2. Example: Tin, aluminium, and other metal cans, Plastic bags etc.
-
-
-
-
-