
Science - Class 7 (C ...

Topic outline
-
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science PDF free download, NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals, to Study online or download free in PDF form. NCERT Textbook Answers of class 7 science chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals, CBSE Class 7 Science Notes , Question Answers provided for NCERT Science Textbook for Class 7, Class 7 Science Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals Exercises Answers, Class 7th Science, Class 7 Science exams, class 7 science notes, science class 7 notes, ncert class 7 science, Nutrition in Animals class 7 notes pdf, NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals, Downlaod NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science, CBSE Science Class 7 Chapter Wise Solved Q&A, Learn 7th grade science, Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals, NCERT Solutions for Class 7th Science Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals, CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 2 - Nutrition in Animals, Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals class 7 science, Science-Class 7 (CBSE/NCERT)-Chapter 2- Nutrition in Animals - Questions and Answers/Notes/Worksheets – 5 Tags: Class VII - Nutrition in Plants, Grade 7 –Science - CBSE / NCERT – Nutrition in Animals Question Bank for seventh class, Question and Answers free worksheet PDF on Nutrition in Animals, Practice page, Important question and Extra question on Nutrition in Animals for seventh standard, Draw a labeled diagram of digestive system of cow. Draw a labeled diagram showing arrangement of teeth and different type of teeth. Draw a labeled diagram of human digestive system.
-
Nutrition in Animals
Question 104:
What substances are secreted in the stomach?Answer:
The inner lining of the stomach secretes mucus, hydrochloric acid and digestive juices. The mucus protects the lining of the stomach. The acid kills many bacteria that enter along with the food and makes the medium in the stomach acidic and helps the digestive juices to act. The digestive juices break down the proteins into simpler substances.
Question 105:
Boojho and Paheli were eating their food hurriedly so that they could go out and play during the recess. Suddenly, Boojho started coughing violently. Think of the reasons why he was coughing and discuss with your friends.Answer:
The windpipe carries air from the nostrils to the lungs. It runs adjacent to the foodpipe. But inside the throat, air and food share a common passage. During the act of swallowing a flap-like valve closes the passage of the windpipe and guides the food into the foodpipe. If, by chance, food particles enter the windpipe, we feel choked, get hiccups or cough.
Question 106:
How is small intestine designed to absorb digested food?Answer:
The inner walls of the small intestine have thousands of finger-like outgrowths. These are called villi (singular villus). The villi increase the surface area for absorption of the digested food. Each villus has a network of thin and small blood vessels close to its surface. The surface of the villi absorbs the digested food materials. The absorbed substances are transported via the blood vessels to different organs of the body.
Question 107:
What is the role of digestive glands in digestion?Answer:
The various associated glands of digestive system and their role in digestion are as follows:
1. Salivary glands secrete saliva. The saliva breaks down the starch into sugars.
2. Liver secretes bile juice that is stored in a sac called the gall bladder. The bile plays an important role in the digestion of fats.
3. Pancreas secretes digestive juices. It acts on carbohydrates, fats and proteins and changes them into simpler forms.
Question 108:
Fill in the blanks using the words listed below.
[water, front, intestinal, salts, pseudopodia, back, vacuole]
(a) The digestion of all food components is completed by the _____ juice.
(b) Large intestine absorbs_____ and some from the undigested food.
(c) Tongue is attached at the_____ to the floor of the mouth cavity and is free at the
(d) Amoeba pushes out_____ around the food and traps it in a food_____.Answer:
(a) intestinal
(b) water, salts
(c) back, front
(d) pseudopodia, vacuole
Question 109:
Write one similarity and one difference between the nutrition in amoeba and human beings.Answer:
Similarity
In amoeba, digestive juices are secreted into the food vacuole. They act on the food and break it down into simpler substances. Gradually the digested food is absorbed. In human, digestive juices are secreted in buccal cavity, liver and small intestine.
Difference
Amoeba captures its food with help of pseudopodia. In human being, food is taken into the body through the mouth.
Question 110:
Match the organs in column I with the words listed in column II.Column I
Column II
a. Rectum
i Mucus
b. Gall bladder
ii Villi
c. Stomach
iii Taste buds
d. Tongue
iv Faeces
e. Small intestine
v Bile juice
Answer:
Column I
Column II
a. Rectum
i Mucus (c)
b. Gall bladder
ii Villi €
c. Stomach
iii Taste buds (d)
d. Tongue
iv Faeces (a)
e. Small intestine
v Bile juice (b)
Question 111:
How does the stomach work?Answer:
The stomach is a thick-walled bag. Its shape is like a flattened J and it is the widest part of the alimentary canal. It receives food from the food pipe at one end and opens into the small intestine at the other. The inner lining of the stomach secretes mucus, hydrochloric acid and digestive juices. The mucus protects the lining of the stomach. The acid kills many bacteria that enter along with the food and makes the medium in the stomach acidic and helps the digestive juices to act. The digestive juices break down the proteins into simpler substances.
Question 112:
Match the animals in Column I with their mode of feeling listed in Column II.Column I
Animals
Column II
Mode of feeding
a. Housefly
i Biting and chewing
b. Cockroach
ii Suckling
c. Mosquitos
iii Sponging
d. Infants
iv Sucking
Answer:
Column I
Animals
Column II
Mode of feeding
a. Housefly
i Biting and chewing (b)
b. Cockroach
ii Suckling (d)
c. Mosquitos
iii Sponging (a)
d. Infants
iv Sucking (c)
Question 113:
Complete the following table.Answer:
Type of teeth
Number of teeth
Total
Lower jaw
Upper jaw
Cutting and
biting teeth
4 Incisors
4 Incisors
8 Incisors
Piercing and
tearing teeth
2 Canines
2 Canines
4 Canines
Chewing and
grinding teeth
4 Premolars & 6 Molars (Including the wisdom tooth)
4 Premolars & 6 Molars (Including the wisdom tooth)
8 Premolars & 12 Molars (Including the wisdom tooth)
Question 114:
Complete the following table.Name of animal
Kind of food
Mode of feeding
Snail
Ant
Eagle
Humming-bird
Lice
Mosquito
Butterfly
House fly
Answer:
Name of animal
Kind of food
Mode of feeding
Snail
Leaves and insects
Scraping
Ant
Sugar and food particles
Chewing and Scraping
Eagle
Small animals
Capturing and Swallowing
Humming-bird
Nectar
Sucking
Lice
Blood
Sucking
Mosquito
Blood
Sucking
Butterfly
Nectar
Siphoning
House fly
Waste or liquids
Siphoning
Question 115:
Draw a labeled diagram of digestive system of cow.Answer:
Fig from NCERT
Question 116:
Draw a labeled diagram showing arrangement of teeth and different type of teeth.Answer:
Fig from NCERT
Question 117:
Draw a labeled diagram of human digestive system.Answer:
Human Digestive System (Figure taken from NCERT)
Question 118:
Choose the odd one out from each group and give reasons.
(i) Liver, salivary gland, starch, gall bladder
(ii) Stomach, liver, pancreas, salivary gland
(iii) Tongue, absorption, taste, swallow
(iv) Oesophagus, small intestine, large intestine, rectumAnswer:
(i) Starch is the odd one out because it is a carbohydrate whereas all others i.e., liver, salivary gland and gall bladder are the glands.
(ii) Stomach is the odd one out because in stomach, digestion of food takes place whereas others are digestive glands
(iii) Absorption is the odd one out because tongue, taste and swallow all are associated with mouth but absorption process does not occur in mouth.
(iv) Small intestine is the odd one out because small intestine takes part in digestion whereas oesophagus, large intestine and rectum will not take part in digestion.
Question 119:
Following statements describe the five steps in animal nutrition. Read each statement and give one word for each statement. Write the terms that describe each process.
(a) Transportation of absorbed food to different parts of body and their utilisation.
(b) Breaking of complex food substances into simpler and soluble substances.
(c) Removal of undigested and unabsorbed solid residues of food from the body.
(d) Taking food into the body.
(e) Transport of digested and soluble food from the intestine to blood vessels.Answer:
(a) Assimilation
(b) Digestion
(c) Egestion
(d) Ingestion
(e) Absorption
Question 120:
Label the given figure directed in (i) to (iv) and give the name of each type of teeth.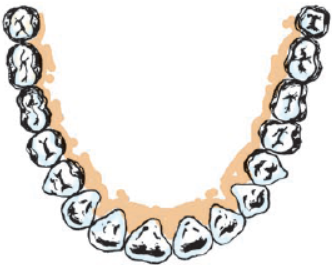
(i) The cutting and biting teeth as ‘A’
(ii) The piercing and tearing teeth as ‘B’
(iii) The grinding and chewing teeth as ‘C’
(iv) The grinding teeth present only in adults as’D’
Answer:
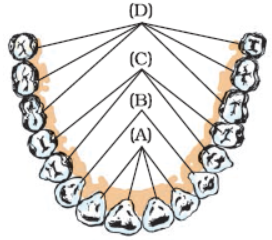
A – Incisors
B – Canines
C – Premolars
D – Molars
Question 121:
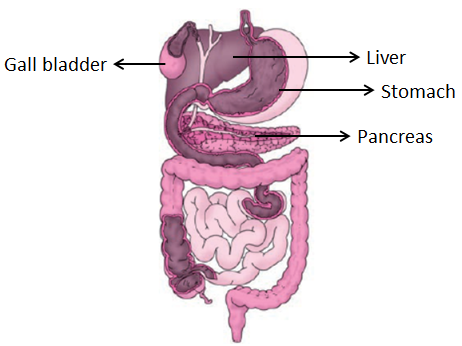
Label the following parts in the figure and name them.
(a) The largest gland in our body.
(b) The organ where protein digestion starts.
(c) The organ that releases digestive juice into the small intestine.
(d) The organ where bile juice gets stored.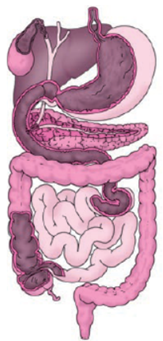
Answer:
(a) Liver
(b) Stomach
(c) Pancreas
(d) Gall bladder
Question 122:
Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions that follow it.
Bile juice is stored in a sac called, gall bladder, located near its organ of secretion, liver. The gall bladder releases the bile juice into the small intestine whenever food reaches there. Though bile juice is devoid of any digestive enzymes, it is required for the digestion of fats. The fats cannot be digested easily because they are insoluble in water and are present as large globules. Bile juice breaks down big fat droplets into smaller droplets. These are then easily digested by the enzymes released from the pancreas.
(a) Which organ secretes the bile juice?
(b) Why is digestion of fats difficult as compared to that of other nutrients?
(c) How does bile juice help in digestion of fat?
(d) Where is the digestion of fat completed?
(e) Does bile juice digest fat completely?Answer:
(a) Liver secretes the bile juice.
(b) Digestion of fats is difficult because fats are insoluble in water.
(c) Bile juice breaks down large fat globules into smaller globules so that they can be easily digested.
(d) Digestion of fat is completed in small intestine.
(e) No. Bile juice does not contain any enzyme.
-